What are Emplorium Flows?
A Flow is a sequence of modular blocks that define a conversational path. You design these paths using an intuitive drag-and-drop builder, allowing for complex logic and personalized visitor experiences. Flows are typically initiated by a Start Condition (similar to a Trigger) and then progress through various Action Blocks based on visitor input or predefined logic.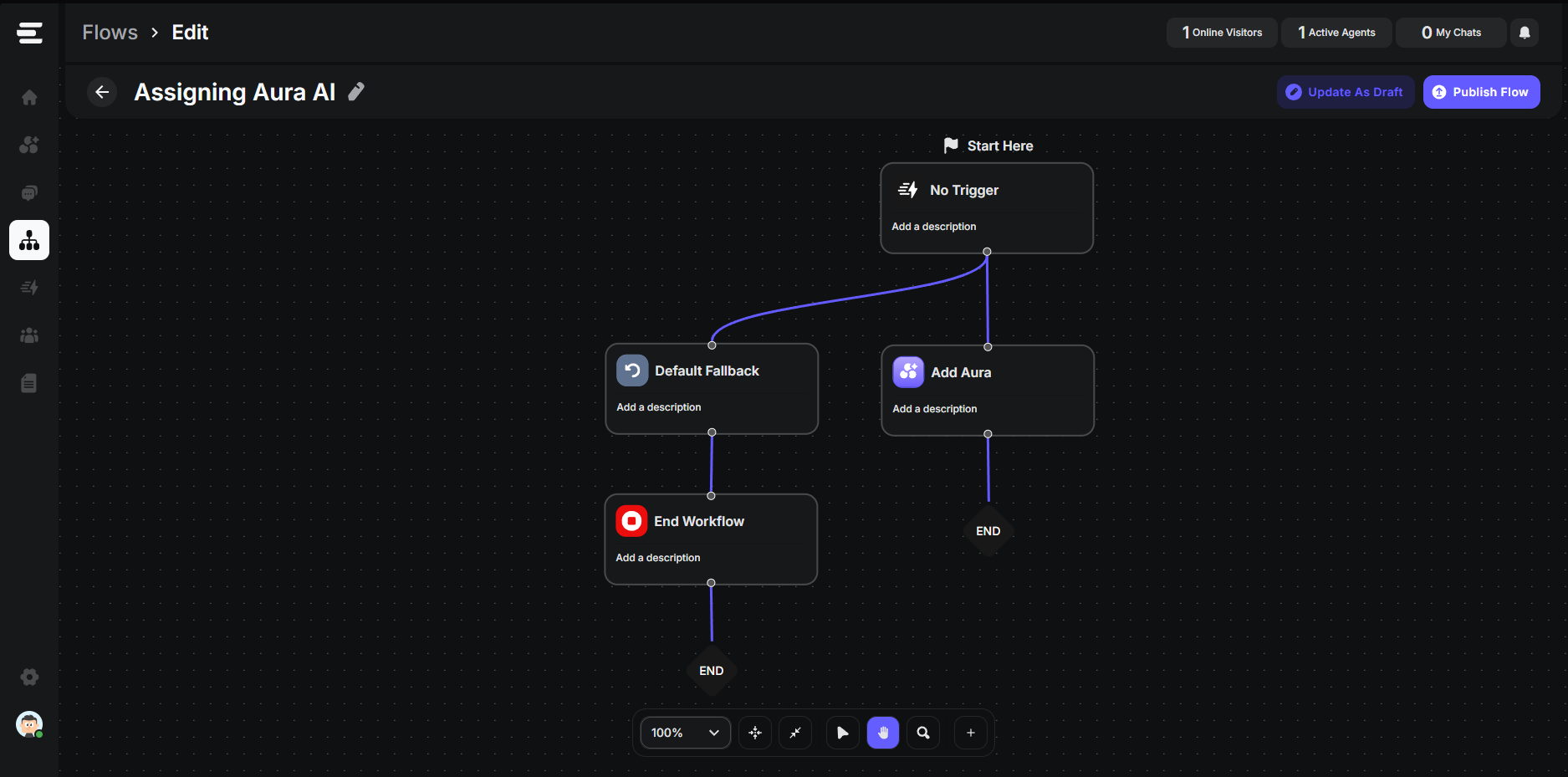
Building a Flow: Start Conditions & Modular Blocks
Creating a Flow involves two main components: defining when the Flow should begin and assembling the series of actions and questions it will execute.1. Start Conditions: Initiating a Flow
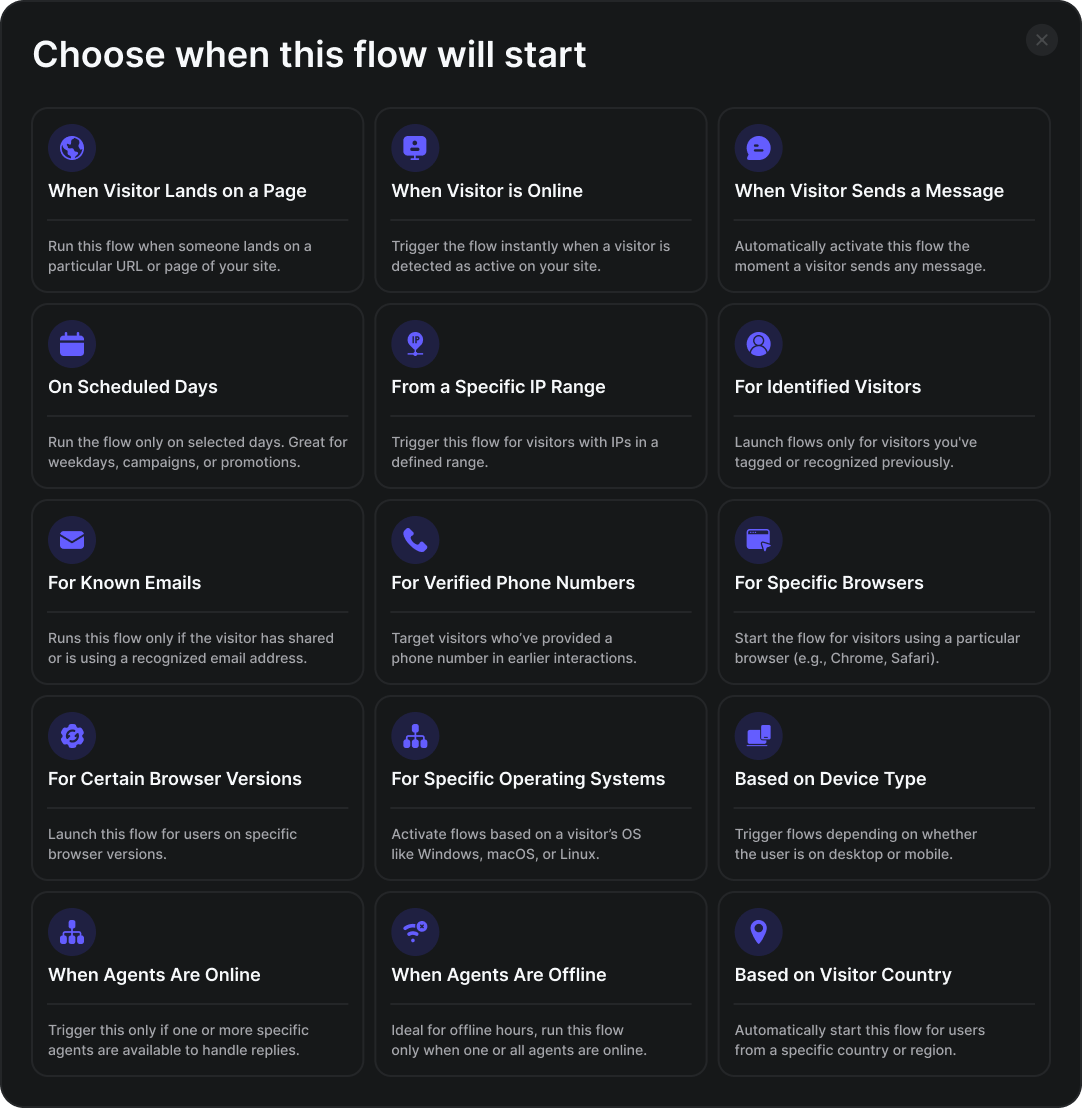
A Flow can be initiated by various visitor actions or environmental factors. These conditions determine when your automated journey begins.Visitor Behavior & Presence
Visitor Behavior & Presence
- When Visitor Lands on a Page: Starts when a visitor arrives on a specified URL.
- When Visitor is Online: Triggers if the visitor is actively Browse your site.
- When Visitor Sends a Message: Initiates the Flow when the visitor sends any message in the chat.
Scheduled & Time-Based
Scheduled & Time-Based
- On Scheduled Days: Allows Flows to run on specific days of the week.
Visitor Identification & Attributes
Visitor Identification & Attributes
- From a Specific IP Range: Targets visitors from a defined IP address range.
- For Identified Visitors: Triggers for visitors whose profiles are known.
- For Known Emails: Initiates for visitors whose email addresses are recorded.
- For Verified Phone Numbers: Starts for visitors with known phone numbers.
- Based on Visitor Country: Triggers based on the visitor’s detected country.
Device & Browser Specificity
Device & Browser Specificity
- For Specific Browsers: Targets users based on their web browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox).
- For Certain Browser Versions: Targets users with specific browser versions.
- For Specific Operating Systems: Triggers for users on particular operating systems (e.g., Windows, macOS).
- Based on Device Type: Initiates for users on Desktop, Mobile, or Tablet devices.
Agent Availability
Agent Availability
- When Agents Are Online: Triggers if at least one agent is available.
- When Agents Are Offline: Triggers if no agents are currently online.
2. Modular Blocks: Designing the Conversation Path
Once a Flow starts, you connect various modular blocks to create the desired user journey. These blocks represent different actions or interactions.Send Message
Send Message
Ask a Question (via bubbles)
Ask a Question (via bubbles)
Send Form
Send Form
Assign Aura AI
Assign Aura AI
Send Data Update
Send Data Update
Branch Logic
Branch Logic
AND/OR operators. This allows the Flow to take different paths based on visitor responses, profile data, or other criteria.Tag Chat
Tag Chat
Escalate to Agent
Escalate to Agent
End Flow
End Flow

Designing Effective Flows: Use Cases & Strategy
Flows empower you to automate complex interactions that go beyond simple trigger-response mechanisms.Common Use Cases for Flows
Lead Qualification & Nurturing
Automated Support Triage
Feedback Collection
Appointment Scheduling
Customer Onboarding & Feature Adoption
Managing & Testing Flows
- Status Toggle: Easily activate or deactivate Flows without deleting them.
- Flow Performance Analytics (Coming Soon): Gain insights into how your Flows are performing, including completion rates, drop-off points, and escalation rates.
- Virtual Visitor: Thoroughly test your Flows in a sandbox environment using the Virtual Visitor to ensure they behave as expected before going live. This is crucial for complex flows.ù
Best Practices for Building Robust Flows
Map Out the Journey First
Keep it Concise & Conversational
Provide Clear Options
Design for Fallback & Escalation
Escalate to Agent blocks at points where the Flow might not be able to resolve an issue, ensuring a smooth handoff.Utilize Branch Logic Smartly
Branch Logic to personalize paths based on visitor input or known profile data, making the Flow more relevant.Test Extensively with Virtual Visitor
Iterate & Optimize (with Analytics)
Next Steps
- Learn About Aura AI - Understand how to assign conversations to your AI agent within a Flow.
- Configure Data Requests & Updates - Integrate external system interactions into your Flows.
- Test Your Flows with Virtual Visitor - Ensure your automated journeys work perfectly before deployment.

